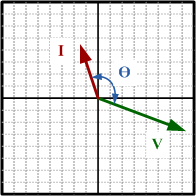
Power Factor (PF) = cos (θ)
Apparent Power (P) = I * V
True Power = P
I = Current
θ = Phase angle
V = Voltage
A calculator is included in the Free
Espresso Engineering Workbook.
|
Power factor measures the phase angle (θ) between the instantaneous voltage
and the instantaneous current in a circuit. Voltage (E) leads current
(I) by 90° in an inductive (L) circuit and voltage
(E) lags current (I) by 90° in a capacitive (C)
circuit.
A popular mnemonic is ELI the ICE man since
E is leading (coming before) I in ELI, and E is lagging (coming after) I in ICE.
| Power
Formulas |
| Apparent Power PA = I
* V [VA]
PA = I2 * R [VA]
PA = V2 / R [VA]
|
True Power (Real) Pt =
I * V * cos (θ) [W]
PT = I2 * Z * cos (θ) [W]
PT = V2 * cos (θ) / Z [W]
|
Reactive Power (Q) PR = I * V *
sin (θ) [VAR]
PR = I2 * Z * sin (θ) [VAR]
PR = V2 * sin (θ) / Z [VAR]
|
| Current I = P / [V * cos (θ)]
I = sqrt {P / [Z * cos (θ)]}
|
Voltage V = P / [I * cos (θ)]
V = sqrt [P * Z / cos (θ)]
|
Impedance Z = V2 * cos (θ) / P
Z = P / [I2 * cos (θ)]
|
|
where
|
P =
PT ± jPR P = power in Watts V = voltage in Volts
I = current in Amps
R = resistance in Ohms (Ω)
Z = impedance in Ohms (Ω)
θ = phase angle between I and V in degrees
PF = power factor
PA = apparent power in Volt·Amps (VA)
PR = apparent power in Volt·Amps (VA)
|
|
|
