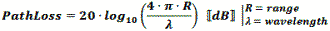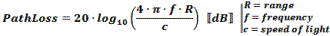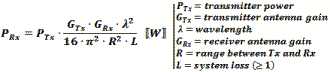Free Space Path Loss - Friis Equation |
||
|
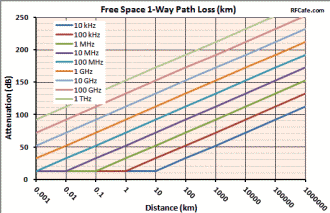
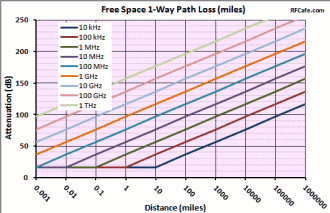
The formula used by RF Workbench accounts for only the diminishing voltage without accounting for absorption or dispersion by the atmosphere. Both a 1-Way and a 2-Way Path Loss Calculator are included in Espresso Engineering Workbook™ for FREE. These equations are valid when the distance is greater than about a wavelength. At distances less than that the electric field is transitioning between near field and far field where, physical factors like antenna dimensions dominate and force the use of electromagnetic field equations. Note: When using these formulas, be sure to keep dimensional units consistent; i.e., do not mix kHz with MHz, mm with inches, etc. It is safer to use base units (e.g., Hz, m) for calculation, then convert result to desired units. 1-Way Power Path Loss Equations (double for 2-way radar signal loss) Friis Equation The Friis Equation (H.T. Friis, 1946) gives a more complete accounting for all the factors from the transmitter to the receiver: Information in the transmitted signal is seldom concentrated at a single frequency, so the path loss will actually be different for every frequency component in the signal. Fortunately, the ratio of the bandwidth to center frequency is usually small enough to not matter. Still, a signal that is transmitted with a constant power across some bandwidth will appear at the receiver with a power slope that decreases at the upper end of the band. Free Space 1-Way Path Loss (km) Free Space 1-Way Path Loss (miles) Here is information on propagation time, radar equation and Doppler.
|
||
 As a transmitted
signal traverses the atmosphere its voltage potential decreases at a rate proportional to the distance traveled (3 dB per distance doubling) and the
power level decreases at a rate proportional to the square of the distance traveled
(6 dB per distance doubling). Note that path loss is equally affected by frequency,
so doubling the frequency also results in 6 dB path loss per distance doubling.
As a transmitted
signal traverses the atmosphere its voltage potential decreases at a rate proportional to the distance traveled (3 dB per distance doubling) and the
power level decreases at a rate proportional to the square of the distance traveled
(6 dB per distance doubling). Note that path loss is equally affected by frequency,
so doubling the frequency also results in 6 dB path loss per distance doubling.